Sedentary Lifestyle and Chronic Diseases: The Link Between Inactivity and Health Risks
In today’s modern society, sedentary lifestyles have become increasingly common. With the rise of technology and the convenience of modern amenities, many people spend the majority of their time sitting at a desk, in front of a screen, or in a car. Unfortunately, this sedentary behavior can have serious implications for our health. Studies have shown a strong link between inactivity and the development of chronic diseases. In this article, we will explore the impact of sedentary lifestyles on our overall health and discuss the various health risks associated with inactivity.
Understanding Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is characterized by a lack of physical activity and prolonged periods of sitting or lying down. This can include activities such as watching TV, playing video games, using a computer, or driving for long periods of time. The human body is designed for movement, and when we fail to engage in regular physical activity, it can have detrimental effects on our health.
The Link Between Sedentary Lifestyle and Chronic Diseases
Research has shown that prolonged periods of inactivity can significantly increase the risk of developing various chronic diseases. Some of the most common health risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle include:
Obesity:
Leading a sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain and obesity. When we sit for extended periods, our metabolism slows down, and we burn fewer calories. Additionally, we are more likely to consume high-calorie, processed foods when we are sedentary, further contributing to weight gain.
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Sedentary behavior is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Prolonged sitting can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and the risk of developing blood clots, all of which can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Regular physical activity is essential for the body to properly utilize insulin and regulate blood sugar levels. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to insulin resistance, which is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes.
Musculoskeletal Problems:
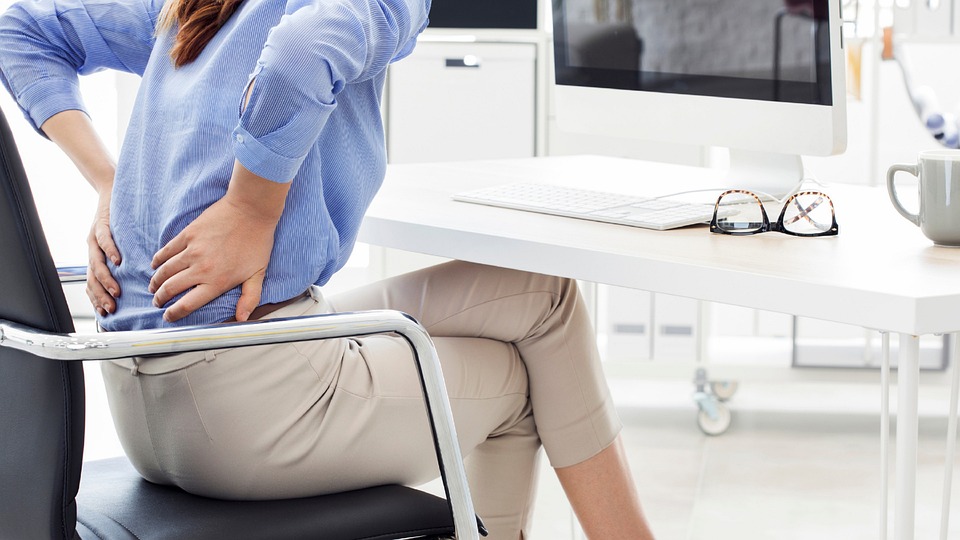
Prolonged sitting can lead to poor posture, muscle imbalances, and stiffness, which can contribute to the development of musculoskeletal problems such as back pain, neck pain, and joint issues.
Mental Health Issues:
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining good mental health. Sedentary lifestyles have been linked to an increased risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: leading a sedentary lifestyle can have serious implications for our health. The link between inactivity and the development of chronic diseases is well-established, and it is essential that we take steps to combat the negative effects of prolonged sitting. Incorporating regular physical activity into our daily routines is crucial for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Whether it’s taking regular walks, participating in exercise classes, or simply standing up and moving around regularly, small lifestyle changes can make a big difference in reducing the health risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle.
FAQs
What is considered a sedentary lifestyle?
A sedentary lifestyle is defined as a lack of physical activity and prolonged periods of sitting or lying down. This includes activities such as watching TV, playing video games, using a computer, or driving for long periods of time.
How can I reduce the negative effects of a sedentary lifestyle?
There are several ways to reduce the negative effects of prolonged sitting. Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, taking frequent breaks to stand up and move around, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting can all help reduce the health risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle.
What are the long-term health risks of a sedentary lifestyle?
The long-term health risks of a sedentary lifestyle include obesity, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, musculoskeletal problems, and mental health issues. Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for reducing these risks and maintaining good overall health.