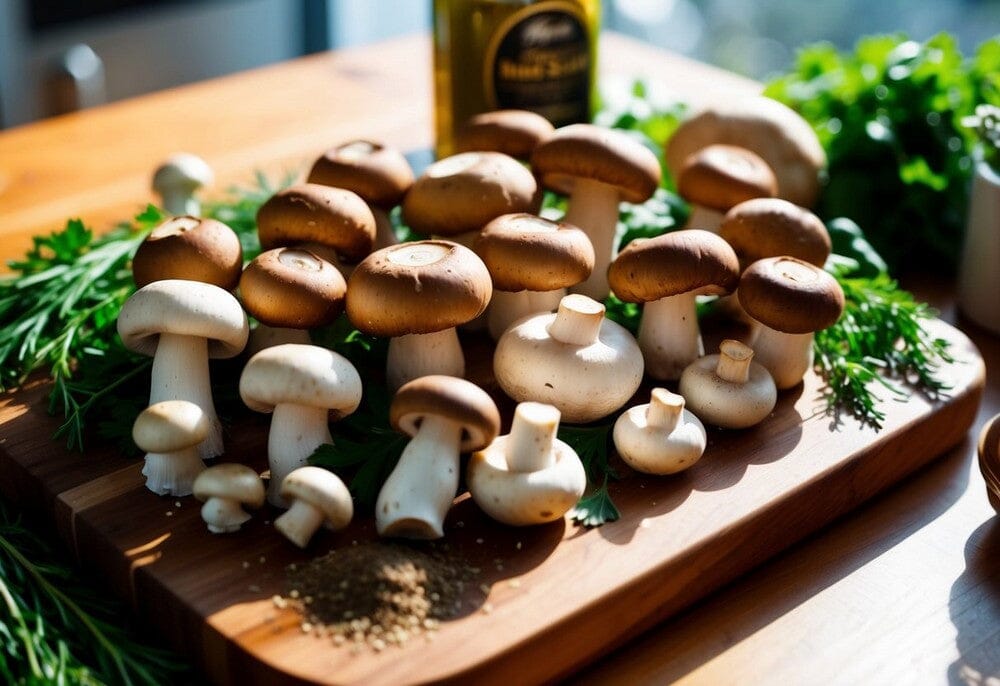
Mushrooms offer a surprising array of health benefits that make them a valuable addition to any diet. Rich in essential nutrients, mushrooms provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall well-being. From enhancing immune function to potentially fighting cancer, the benefits of mushrooms are numerous and well worth exploring.
The nutritional profile of mushrooms includes significant amounts of B vitamins, selenium, and copper, which are essential for energy production and maintaining a healthy immune system. Additionally, their low-calorie content and high fiber levels make them a great choice for weight management and digestive health.
Mushrooms also contain bioactive compounds, such as beta-glucans, that have been studied for their potential to reduce inflammation and boost the immune system. By incorporating mushrooms into daily meals, individuals can take advantage of these powerful health-promoting properties.
Nutritional Profile of Mushrooms
Mushrooms are low in calories and a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals. They provide a balanced array of macronutrients and support overall health with their nutrient composition.
Vitamins and Minerals in Mushrooms
Mushrooms are packed with essential vitamins and minerals. Vitamin D, which supports bone health, is one of the most notable. They also contain high levels of B vitamins such as niacin, riboflavin, and pantothenic acid, which play roles in energy production and brain health.
Minerals like potassium, selenium, copper, and iron are abundant in mushrooms. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure, while selenium has antioxidant properties. Copper is crucial for heart health, and iron is essential for oxygen transport in the bloodstream.
Caloric Content and Macronutrients
Mushrooms are low in calories, making them a great addition to any diet. A typical serving contains around 20 calories. They provide a good amount of protein and fiber, which are essential for muscle maintenance and digestive health.
Mushrooms are low in fat and contain moderate amounts of carbohydrates. These carbs include both simple sugars and dietary fiber, contributing to satiety and digestive health. Their low calorie and fat content, combined with their nutrient density, make them a beneficial food for maintaining a healthy diet.
Health Benefits of Mushroom Consumption
Mushrooms provide an array of health benefits, including supporting the immune system and potentially offering cancer-fighting properties. They also contribute positively to heart health, blood pressure regulation, blood sugar control, weight management, and gut health.
Immune System Support
Mushrooms can enhance the immune system. They contain beta-glucans, which are compounds known to boost the body’s natural defenses. Antioxidants in mushrooms, such as selenium and ergothioneine, help protect cells from damage, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Consuming them regularly may improve the immune response, making the body more resilient against infections and diseases.
Potential Cancer-Fighting Properties
Certain varieties of mushrooms, like shiitake and maitake, have shown potential in cancer prevention and treatment. Polysaccharides, specifically beta-glucans, stimulate immune function and may inhibit the growth of cancer cells. Additionally, antioxidants in mushrooms help neutralize free radicals, reducing the risk of cancer development.
Beneficial Effects on Heart Health
Mushrooms are beneficial for heart health. They are low in fat and contain no cholesterol, making them an excellent choice for a heart-healthy diet. Bioactive compounds in mushrooms, such as sterols and beta-glucans, can help lower cholesterol levels. Potassium and fiber in mushrooms also contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Mushrooms and Blood Pressure Regulation
High potassium content in mushrooms helps regulate blood pressure. Potassium counteracts sodium’s effects and relaxes blood vessel walls, promoting better blood flow. This mineral also helps balance fluids in the body, which is essential for blood pressure control. Regular intake of potassium-rich foods like mushrooms can contribute to long-term cardiovascular health.
Mushrooms’ Role in Blood Sugar Control
Mushrooms have a low glycemic index, making them suitable for blood sugar control. They contain polysaccharides, which can slow down glucose absorption, reducing blood sugar spikes after meals. Additionally, the fiber content in mushrooms helps manage blood sugar levels by slowing glucose release into the bloodstream, benefiting individuals with diabetes.
Weight Management and Satiety
Low in calories and high in fiber, mushrooms are ideal for weight management. Their high water content also makes them filling, promoting satiety and reducing overall calorie intake. Incorporating mushrooms into meals can help in maintaining a healthy weight and prevent overeating. This can be particularly beneficial for those looking to manage their weight effectively.
Gut Health and Digestion
Mushrooms contribute to gut health and digestion. They are rich in dietary fiber, which aids in regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. Prebiotics in mushrooms support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing the digestive system’s overall health. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for nutrient absorption and immune function.
Mental and Brain Health
Mushrooms can positively impact mental and brain health. They are rich in antioxidants, which protect brain cells from damage and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Certain mushrooms, like lion’s mane, have been studied for their potential to stimulate nerve growth and improve cognitive function. Regular consumption may contribute to better brain health and cognitive performance.
Types of Edible Mushrooms and Their Unique Benefits

Edible mushrooms come in various types, each offering unique health benefits. Understanding these specific varieties can help in making healthier dietary choices.
Common Varieties and Their Health Properties
Oyster Mushrooms: These fungi are known for their high content of antioxidants and have compounds believed to lower cholesterol levels. Additionally, they are rich in vitamins B and D.
Shiitake Mushrooms: Shiitake mushrooms contain a compound called lentinan, which is noted for its potential immune-boosting properties. They also offer a good source of iron.
Maitake Mushrooms: Often referred to as “Hen of the Woods,” maitake is studied for its potential to regulate blood sugar and support immune function. This variety is also rich in vitamins and minerals.
Cremini and Portobello Mushrooms: These two types are botanically the same species but differ in maturity. Cremini mushrooms are young, while portobellos are their mature form. Both are excellent sources of selenium and potassium.
Wild Mushrooms: Varieties like chanterelle and enoki provide different textures and flavors. Chanterelles are rich in vitamin D, aiding in calcium absorption. Enoki mushrooms contain antioxidants that may help combat inflammation.
Comparative Benefits of Different Species
When comparing these species, it’s essential to consider their unique nutrient profiles:
- Oyster vs. Shiitake: While both offer immune benefits, shiitake mushrooms have a more significant amount of iron and lentinan. Oyster mushrooms may be superior in terms of antioxidants and cholesterol management.
- Maitake vs. Cremini: Maitake mushrooms stand out for their blood sugar regulation and immune support. On the other hand, cremini mushrooms provide more selenium and potassium, beneficial for maintaining a healthy heart.
- Portobello vs. Wild Mushrooms: Portobello mushrooms are easier to find and excellent for grilling, with significant amounts of selenium. Wild mushrooms like chanterelle and enoki add diversity to the diet and offer nutrients like vitamin D and antioxidants for inflammation control.
By incorporating a range of these mushroom types, one can leverage their diverse benefits for improved health and well-being.
Mushrooms in Different Diets and Cuisine
Mushrooms offer versatility in various diets and cuisines. They are rich in dietary fiber and umami, making them suitable for salads, vegan meals, and as meat substitutes. Their storage and selection also impact their flavor and nutritional value.
Incorporating Mushrooms into Meals
In many dishes, mushrooms add a unique texture and flavor. They can be sautéed with garlic and olive oil, then mixed into a pasta dish for a savory burst. Adding mushrooms to a salad brings an earthy tone, especially with varieties like shiitake or portobello.
When grilled, mushrooms can enhance sandwiches and wraps. They also serve well in soups and stews, boosting umami and richness. Versatility is key, as they fit into breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
Mushrooms as Meat Alternatives
For those on vegan or vegetarian diets, mushrooms often serve as a meat substitute. Portobello mushrooms, in particular, are thick and hearty, making them ideal for burgers.
Table: Example Mushroom Meat Substitutes
| Mushroom Type | Dish |
|---|---|
| Portobello | Burgers, Grilled dishes |
| Chestnut | Stews, Casseroles |
| Shiitake | Stir-fries, Soups |
These mushrooms contain dietary fiber and proteins, adding nutritional value while mimicking meat textures.
Selection and Storage Tips
Choosing the right mushrooms ensures quality dishes. Fresh mushrooms should be firm, with a smooth texture. Avoid any that appear slimy or have dark spots.
Storage Tips:
- Refrigeration: Store in a paper bag to allow air circulation.
- Usage: Use within a week for best flavor and texture.
- Freezing: For long-term storage, clean and slice mushrooms, then freeze in airtight containers.
Proper selection and storage preserve their flavor and nutrients, ensuring they remain a valuable addition to meals.
Safety and Considerations in Mushroom Consumption

Mushroom consumption necessitates awareness about the potential dangers of poisonous varieties and understanding possible side effects and interactions. Being informed helps in making safer dietary choices.
Recognizing and Avoiding Poisonous Varieties
Identifying edible mushrooms can be challenging due to their resemblance to toxic ones. Foragers should avoid picking wild mushrooms unless they have extensive knowledge or expertise.
Some dangerous varieties include the Amanita species, responsible for most severe mushroom poisonings. Symptoms of poisoning can involve nausea, vomiting, and in severe cases, organ failure.
Using guides or consulting experts is crucial. The saying “When in doubt, throw it out” underscores the importance of caution. Cultivated mushrooms from reputable sources are safer choices for consumption.
Possible Side Effects and Interactions
While many mushrooms are nutritious, they can cause side effects or interact with medications. Common side effects include digestive issues such as bloating and gas. Certain types, like shiitake, may cause skin rashes in sensitive individuals.
Interactions with alcohol can lead to adverse reactions. For example, Coprinus comatus (inky cap) mushrooms can cause flushing and palpitations if alcohol is consumed shortly after.
Some mushrooms, particularly psilocybin mushrooms, can induce hallucinations and are illegal in many areas. Individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications should consult healthcare professionals before adding mushrooms to their diet.
This cautious approach ensures a balanced and safe enjoyment of mushrooms’ health benefits.
Emerging Research and Potential Therapeutic Uses
Recent studies have highlighted the promising role of mushrooms in disease prevention and as potential therapeutic agents. These insights open new avenues for their use in medicinal food and healthcare.
Studies on Mushrooms and Disease Prevention
Research into mushrooms reveals a wealth of bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides and beta-glucans. These compounds have shown potential in preventing various diseases.
For instance, beta-glucans are linked to immune system modulation, according to a review conducted in Japan. Another study found that certain mushroom extracts possess strong antioxidant properties, which help fight oxidative stress, a known contributor to chronic diseases.
Such findings underline mushrooms’ potential health benefits, making them a focal point for scientists exploring natural disease prevention methods.
Future Prospects in Medicinal Mushrooms
Medicinal mushrooms are gaining attention for their potential therapeutic applications. Ongoing research indicates that they may be used to develop new treatments for a variety of conditions.
For example, polysaccharides extracted from mushrooms are being studied for their anti-cancer properties. Additionally, specific mushrooms are being investigated for their role in managing diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
As research progresses, the integration of medicinal mushrooms into therapeutic strategies could become more common, offering innovative solutions in healthcare.
Mushroom Supplementation and Extracts
Mushroom supplementation offers concentrated bioactive compounds, while extracts provide a potent form for targeted health benefits. Evaluating the differences between supplements and whole food consumption, and selecting quality products is important for optimal benefits.
Supplements vs. Whole Food Consumption
Supplements provide concentrated doses of mushroom bioactive compounds. Whole mushrooms, on the other hand, are a nutritious vegetable rich in fiber and essential nutrients.
Supplements can be convenient for those seeking specific health benefits, like immune support or cognitive function. They may contain extracts like polysaccharides and beta-glucans, which are key in bioactive effects.
Whole food consumption allows for a broader intake of nutrients. Mushrooms in their natural form offer dietary fibers, essential vitamins, and minerals. Consuming them as part of a varied diet ensures a more holistic nutritional approach.
How to Choose Quality Mushroom Supplements
Mushrooms are a powerhouse of nutrients and health benefits, making them a valuable addition to any diet. From supporting the immune system and heart health to aiding in weight management and digestive health, the range of benefits mushrooms provide is vast and varied.
To maximize these advantages, consider incorporating a variety of mushrooms into your meals or exploring supplements designed to harness their powerful properties.
Health Nutrition offers a Mushroom Immune Booster supplement that provides natural immune system support, fights inflammation, and boosts energy levels, all with safe and all-natural ingredients. Discover how this supplement can enhance your well-being by visiting Health Nutrition’s range of products today.
Source link