Movement Matters: The Health Crisis of a Sedentary Life
In today’s fast-paced world, the convenience of technology has made life easier but at a cost: an increase in sedentary behavior. Movement is an integral part of our physical and mental well-being. However, prolonged inactivity has far-reaching consequences that are becoming increasingly alarming. This article discusses the health crisis stemming from a sedentary lifestyle and how we can incorporate movement into our daily routines.
The Sedentary Lifestyle Epidemic
According to recent studies, a significant portion of the population spends over 8-10 hours seated each day. From working in front of computers to binge-watching series on weekends, the implications of a sedentary lifestyle are severe. Public health authorities classify sedentary behavior as any waking activity characterized by low energy expenditure while in a sitting or reclining posture. This description encompasses a good portion of modern life.
Statistics That Shock
In the United States alone, nearly 80% of adults fail to meet recommended levels of physical activity. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), physical inactivity is one of the leading risk factors for global mortality. This trend is not limited to adults; a worrying rise in sedentary behavior among children and adolescents is evident as well.
The Health Risks of Inactivity
The consequences of a sedentary lifestyle extend far beyond mere discomfort. Not only does a lack of movement contribute to physical ailments, but it also significantly impacts mental health. Below are some of the major health risks associated with prolonged inactivity:
1. Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
Inactivity is linked to a host of chronic conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and various types of cancer. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels, creating a perfect storm for cardiovascular problems.
2. Mental Health Issues
Many people may not realize that inactivity can adversely affect mental health. Studies indicate that individuals who are less physically active are more likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety. Movement stimulates the release of endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters, making regular physical activity crucial for mental well-being.
3. Musculoskeletal Pain
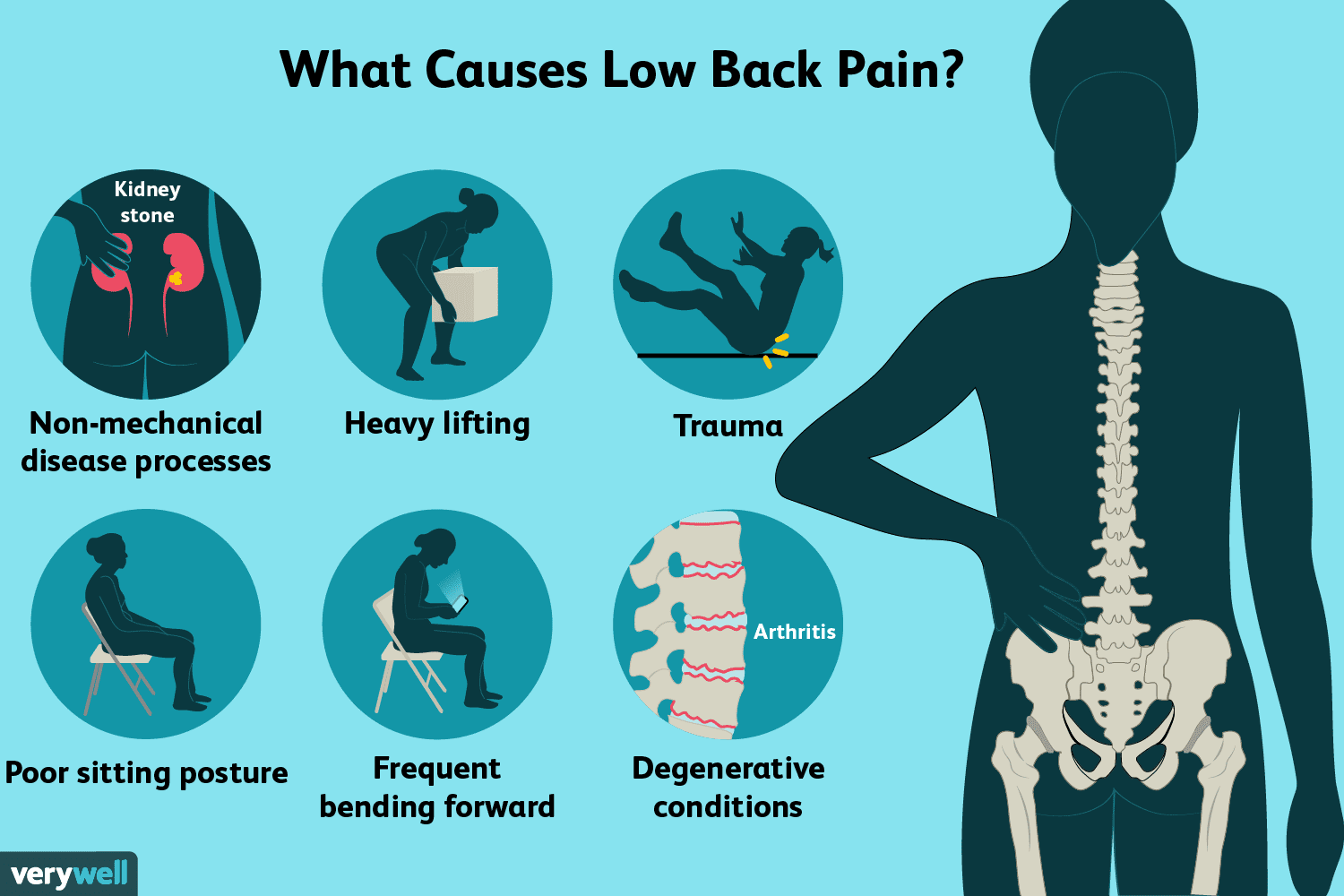
Prolonged periods of sitting or lying down can lead to muscular imbalances, strain, and chronic pain. Conditions such as lower back pain, neck pain, and joint issues are commonly associated with sedentary lifestyles. Regular movement helps maintain muscle flexibility, strength, and overall function.
How to Combat Sedentary Behavior
Breaking free from a sedentary lifestyle requires awareness and intentionality. Here are some strategies to incorporate movement into your day:
1. Set Daily Movement Goals
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) movement goals can provide structure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, as recommended by health guidelines.
2. Use Technology to Your Advantage
Utilize apps or wearable devices to track your physical activity and set reminders to move. Many smartwatches and fitness trackers remind you to stand and move after long periods of inactivity.
3. Incorporate Movement into Daily Routines
Find opportunities to move during your day. Take short breaks every hour to stretch or walk around. Opt for stairs instead of elevators, park further away from your destination, or even walk during phone calls or meetings.
4. Join a Community
Being part of a physical activity group can provide motivation and accountability. Whether it is a local running club, yoga class, or online support group, social interaction can help sustain your commitment to movement.
5. Make Movement Enjoyable
Choose activities you enjoy. Whether it’s dancing, swimming, or hiking, finding joy in movement will make it easier to integrate into daily life.
Conclusion
Movement is crucial for both physical and mental health, yet the modern lifestyle poses challenges in combating inactivity. Understanding the risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle is the first step towards change. By implementing simple strategies to incorporate movement into our daily routines, we can not only improve our health but also enhance our overall quality of life. The call to action is clear: movement matters. Let’s prioritize it!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a sedentary lifestyle?
A sedentary lifestyle is characterized by prolonged periods of low energy expenditure while sitting or reclining, including activities like watching TV, working at a desk, and even driving.
2. How much physical activity do I need each week?
Health guidelines recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week for adults.
3. Can short bursts of activity help?
Yes! Short bursts of physical activity throughout the day can contribute to your overall fitness and reduce the risks associated with prolonged inactivity.
4. What are some simple ways to get moving during the day?
Simple ways to incorporate movement include taking short walking breaks, choosing stairs over elevators, and setting reminders to stand every hour.
5. How can I stay motivated to be more active?
Joining a class, setting achievable goals, or finding an activity you genuinely enjoy can help maintain motivation. Tracking your progress can also provide a sense of accomplishment.